Abstract: (Watch Video)
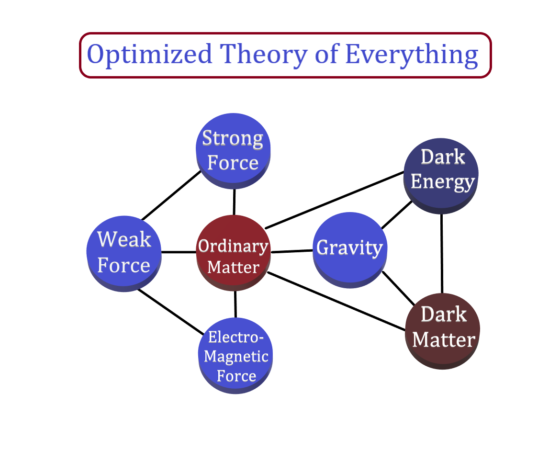
As per the current understanding of the Universe, the entire Universe is made up of dark energy (68%), dark matter (27%) and ordinary matter (5%). These three interact with one another by one or more of the four forces: strong force, weak force, electromagnetism and gravity.
According to the Optimized ToE (O-ToE), all the experimentally measured interactions of dark energy, dark matter and ordinary matter with one another are explained as the derived interactions which are the outcomes of the definite basic interaction. Four basic forces have also been proven as the derived forces. All elementary particles of the standard model have been proven as the derived particles of the well-defined primary building blocks which are primarily constituted by the definite total quanta of energy (tqE) and the definite total quanta of mass (tqM).
This theory is an optimization of all the concepts of classical mechanics and quantum mechanics. It explains all the concepts of quantum mechanics by using the concepts of classical mechanics and thermodynamics. This merge is the most essential for the unification of gravity with the other three forces. This theory can bridge the gap between quantum mechanics, classical mechanics and general relativity. It is helpful to explain presently unknown properties and interactions of dark energy and dark matter with each other as well as with ordinary matter.
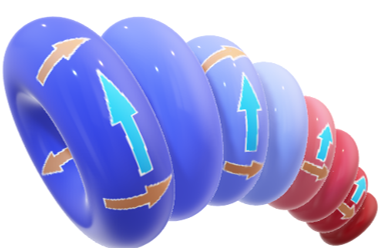
Structure of Primary Building Block (PBB)
According to this theory, the primary building block is made up of definite quanta of dark energy and definite quanta of dark matter which continuously rotates circularly as per right-hand thumb rule. Within PBB, bended (bent) cone-shaped dynamic tunnel is made up of a number of doughnuts shaped circular tracts of different radius organized in descending order. On each of these circular tracts, definite quanta of dark energy rotate circularly in the definite direction with definite frequency. Dark matter is rotated within the dynamic tunnel in the direction of thumb as per right-hand thumb rule, whereas outside of the tunnel, dark matter moves in the opposite direction. The direction of curled fingers suggests the direction of rotation of quanta of dark energy.
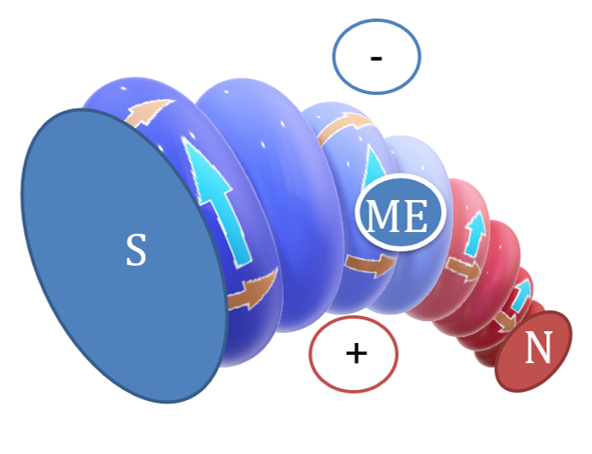
Polarized substructures within PBB
Three pairs of polarized substructures are present within PBB. Each of these pairs of substructures is responsible to exhibit electric property, magnetic property and matrix property of PBB.
On the base of characteristics and spatial arrangement of PBBs as compared to its nucleus, they are subcategorized in 3 types.
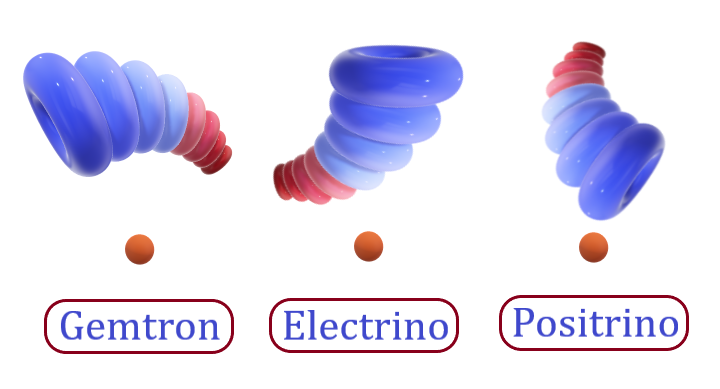
Three types of PBB
Among these three types, Energy communicating Building Block (ECBB) has a relatively higher affinity towards energy as compared to mass. It is a carrier of long-acting forces like gravity and electromagnetism. So, it is also termed as Gemtron. They are constructive units in the formation of ether, photons, electron neutrinos, electrons, positrons and nucletrons. They are constructive units of all elementary particles of the standard model. In nature, it exists either in individual form or in fused form with the other two types of PBB.
Energy and mass managing Building block (EMMBB) has an equal affinity towards energy and mass. They are constructive units in the formation of electrons and nucletrons. Along with electrons, this building block is a constructive unit of all negatively charged elementary particles of the standard model. So, it is also termed as Electrino. In nature, it exists only in fused form with the other two types of PBB.
Mass organizing Building block (MOBB) has a relatively higher affinity towards the mass as compared to energy. They are constructive units in the formation of positrons and nucletrons. Along with positrons, this building block is a constructive unit of all positively charged elementary particles of the standard model. So, it is also termed as Positrino. In nature, it exists only in fused form with the other two types of PBB.
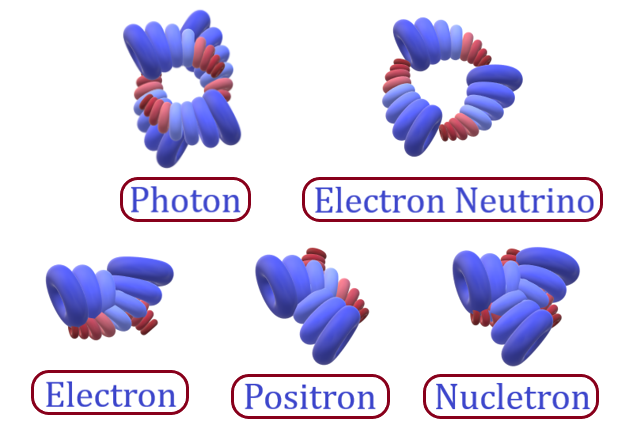
Different types of SBB
Secondary Building Block is made up of two or more PBB of the same or different types within its structure. So, the circular rotation of dark energy and dark matter are carried out in multiple directions within the structure of SBB due to the presence of two or more PBB within it. Some of the SBBs are made up by the fusion of two or three PBBs of different types. So, these SBBs possess definite quanta of ordinary matter having static nature due to the accumulation of dark matter at the point of interception of two (or three) fused PBBs. Examples of SBB are Photons, Electron Neutrinos, Electrons, Positrons and Nucletrons.
Tertiary building blocks are made up by fusion of two or more PBB and SBB of the same or different types within its structure. So, due to the circular rotation of dark energy and dark matter in multiple directions, these TBBs possess definite quanta of ordinary matter having static nature due to the accumulation of dark matter at the point of interception of two or more fused PBBs and SBBs. Examples of TBB are all elementary particles of the standard model (i.e. quarks, leptons and bosons) which are not included in SBBs.
Quaternary building blocks are made up by fusion of two or more PBB, SBB and TBB of same or different types within its structure. So, due to the circular rotation of dark energy and dark matter in multiple directions, these QBBs possess definite quanta of ordinary matter having static nature due to the accumulation of dark matter at the point of interception of two or more fused PBBs, SBBs and TBBs. Examples of QBB are all hadrons (i.e. baryons and mesons) which are derived by fusion of PBB, SBB and TBB.
By this theory, the number of solutions are provided with underlying interactions between various BBs for many unsolved problems of physics. Ether having the matrix of Gemtrons explains all the concepts of the general theory of relativity including time dilation and length contraction by extrapolating the concept of thermodynamics for the matrix of gemtrons. Within the quantum realm, this ether is responsible for the formation of quantized energy levels which not only traps electrons within atom but also prevents their entrapment within the nucleus.
Matrix of gemtrons spread across the multiverse solves all the problems related to electromagnetic radiation like its nature (i.e. Particle form or waveform), its absorption and emission in definite quanta of energy as a photon by definite electron within an atom, its wave properties like reflection, refraction, double refraction, diffraction and polarization, its constant velocity within space, its red and blue shift due to the relative movement between astronomical objects and earth, bending of EMR in presence of the massive object, its quantum tunneling, its production by low energy annihilation of electron and positron, pair production within the nucleus as well as the photoelectric effect due to photon.
The interactions between Gemtrons, Electrons, Positrons and Nucletrons are responsible for short-acting forces like weak force (interaction) between protons and strong force between quarks (within nucleons) and between nucleons (within the nucleus), electron capture or positron emission within the proton-rich nucleus, pair production and β– emission within the neutron-rich nucleus, nuclear fission, nuclear fusion, production of subatomic particles by high energy annihilation of electrons and positrons, the formation of subatomic particles by the collision between protons in Large Hadron Collider and decay of subatomic particles within particle accelerators.
The interaction between electrons and gemtrons are responsible for arrangement of electrons within definite quantized energy levels of atom, arrangement of electrons in covalent bond formation, definite molecular geometry of each molecule (including definite bond length, bond angle and torsional angle in between constituted atoms) and definite vibrational, bending and rotational frequency for the covalently bound two atoms, collision between two atoms and formation of heat, collision between two atoms and formation of EMR, process of fluorescence and phosphorescence, effect of molecular quenching, as well as orientation of free electrons in metal wire in presence or absence of voltage difference, effect of magnet on its surrounding medium during its static and dynamic condition, electromagnetic induction processes like AC generator, self-induction and mutual induction, orientation and movement of electrons (in cathode ray tube or particle accelerator) in absence/presence of electric fields and magnetic fields.